Forming Section (until dry-line)
Packages » Forming
Description
The forming section simulator simulates the forming section just after jet impingement takes place and stretches until the dry-line when air comes to the system and new phenomena take place.
The process is basically of filtration with the difference that the final properties of the cake are of essential relevance. Hence, the filtration process is driven by a pressures. They are viz. dynamic pressure from the jet landing on the wire, gravitational head due to the suspension height and applied vacuum either directly or by foils.
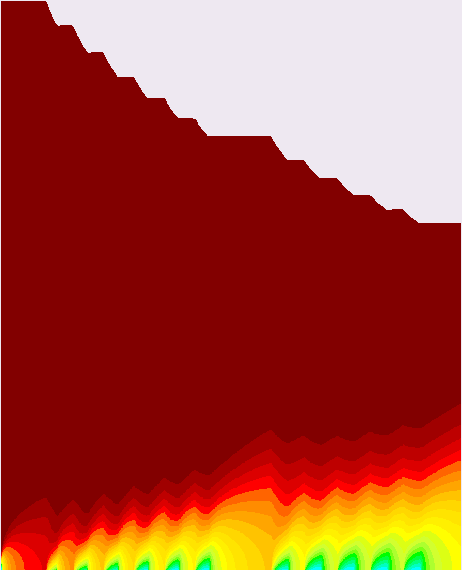
The drive force from the different contributions faces a flow resistance, and their interaction results in a dewatering rate. The flow resistance comes from momentum loss as water flows through the fibre cake (see figure in the box). The inverse of this flow resistance is called permeability, which is dependent on pulp properties and concentration. There are several constitutive equations describing the dependent of this quantities. The wire and the interaction between wire and the fibre cake also have negative contributions for water flow.
Momentum is transfered to the fibre cake, which becomes more compressed the closer it gets to the wire. The punctual concentration achieved is determined by stress-strain (concentration) expressions.
Not all the fibre material, fines and fillers remain on the wire. The fraction of the material that stays on the wire is called retention.
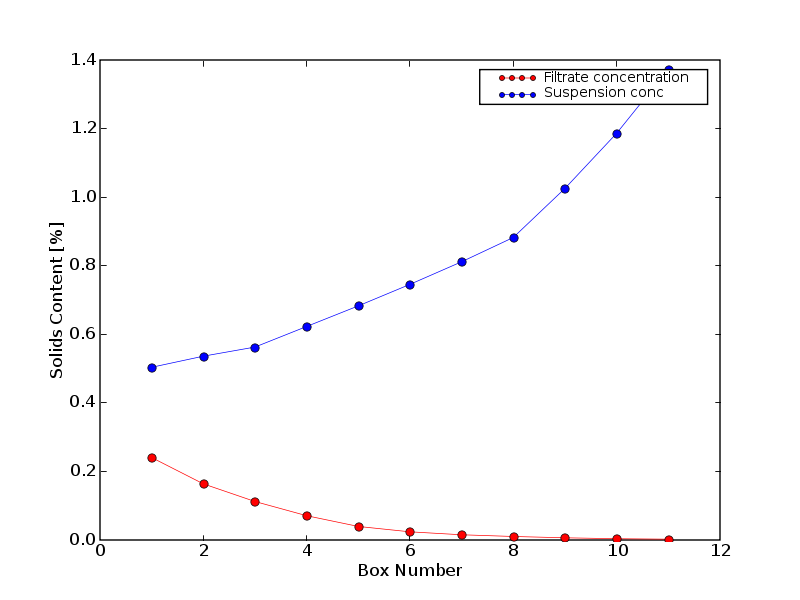
Presently the simulator calculates the dewatering rate, the concentration, white water concentration, retention etc. along Fourdrinier and Hybrid formers. Examples of the results that can be obtained are shown in the figure below. The figure below shows the average concentration of the material on the wire and the white water concentration.
And the figure below shows the deposited fibre mat as a function of position.
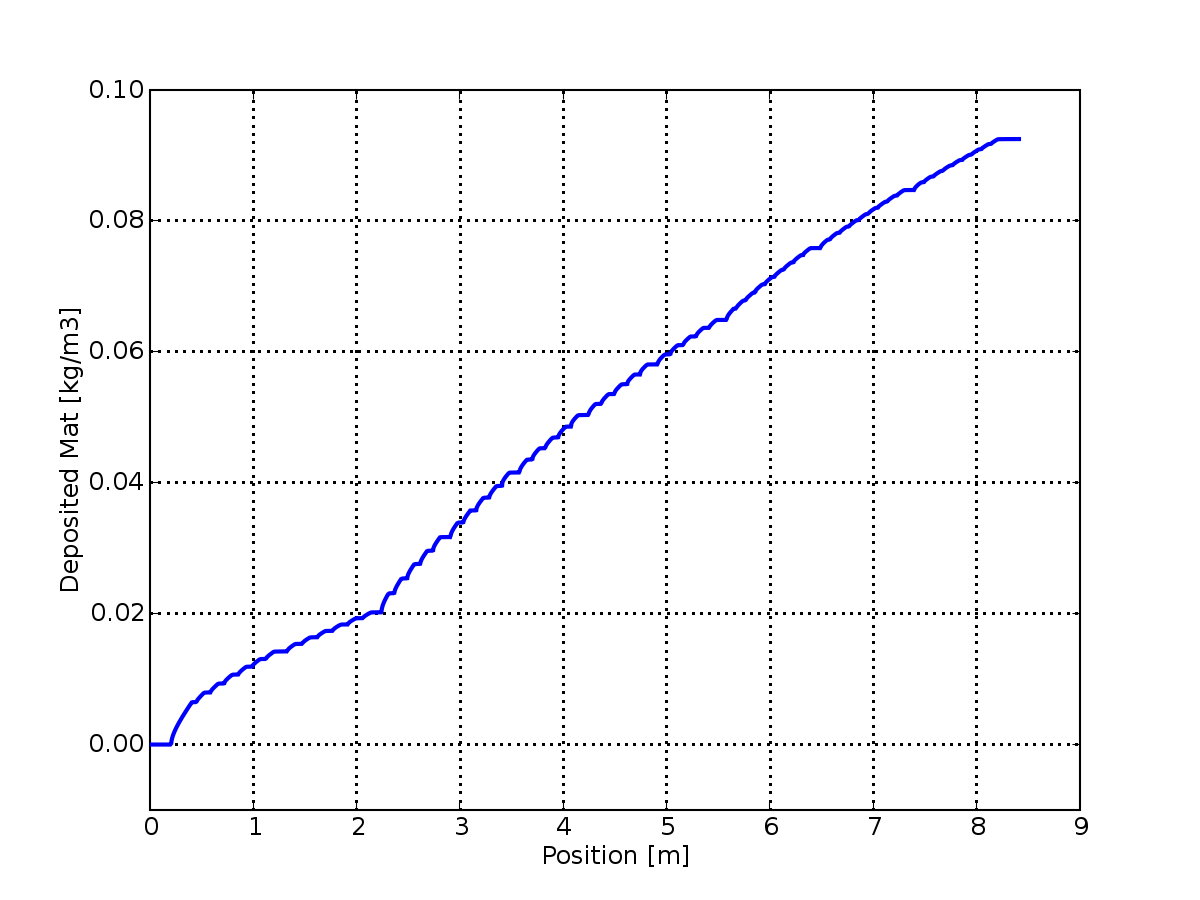
The simulator takes into account to the fast variations of vacuum pulses applied along the forming section. It is therefore possible to study the influence of different vacuum profiles, adding new vacuum boxes, etc. Roll and blade formers are under implementation.
» Download presentation at Paper Physics 2006 on validation of PaperSim.
For more information, please, contact:
Vinicius Lobosco, PhD, +46 73 925 8476
or
Klas Samuelsson, PhD, +46 70 668 5515